
The Largest End-to-End Omnichannel Enabler In Southeast Asia
Trusted by the world’s leading brands





SE Asia’s Leading
End-to-End Omnichannel Enabler
We are the leading enabler in Southeast Asia, trusted by the world’s top brands. Our end-to-end enablement solution allows you incredible speed-to-market time, regional expertise, and global standards. Built to scale, without all the additional costs and pain of having to build in-house infrastructure.
COMPETE FASTER by
#1 E-commerce Business Services in SE Asia
Managed Services
Our e-commerce Managed Services makes it easy for your brands to enter a market and scale your online business without the costly need of building your infrastructure or training internal teams. Our Managed Services are cost-efficient and built to scale with the most innovative team in the region. Partner with aCommerce to get the best results for your e-commerce business.
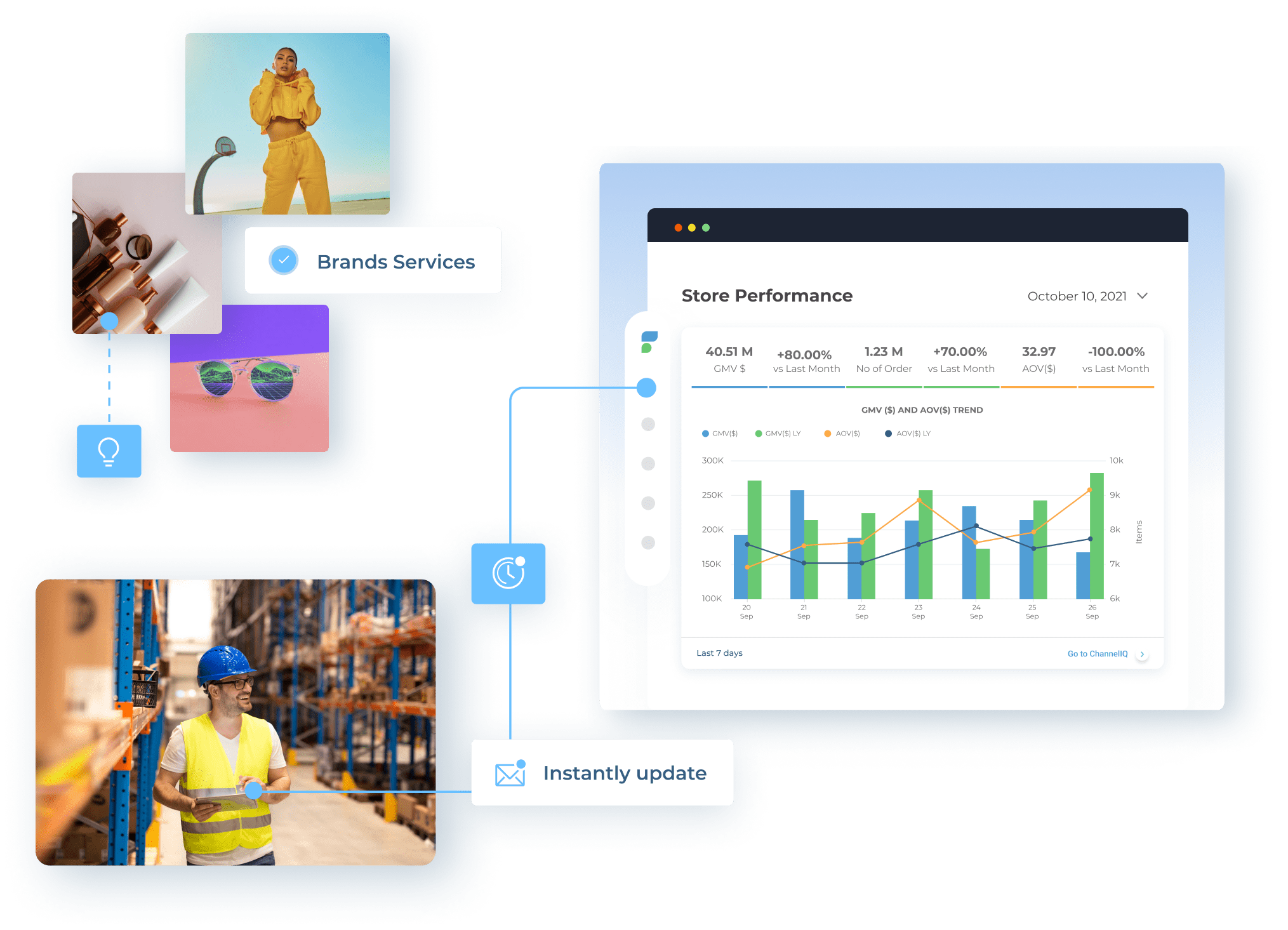
The harness the empower of e-commerce
Simplfied and Unified
E-commerce Enablement Platform
EcommerceIQ is a cutting-edge e-commerce management solution by aCommerce that provides you with a 360° view of their business and a complete toolset to service all business units and e-commerce processes including accounting, merchandising, performance marketing, account management, fulfillment and logistics, omnichannel order management, and business intelligence.
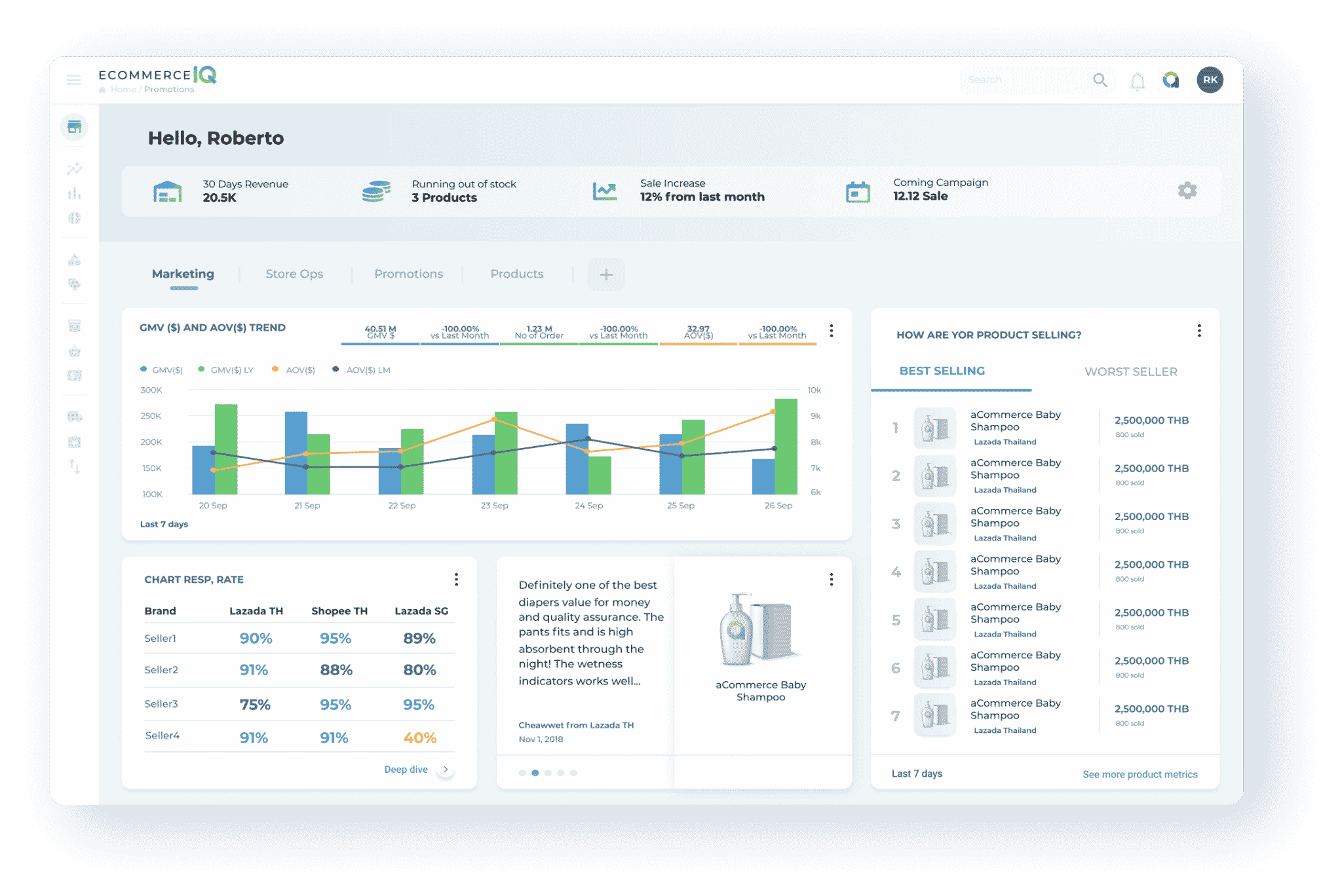
360° view of your business
All-in-One E-commerce Management Platform
Using EcommerceIQ, brands can easily monitor and control every aspect of their e-commerce business across multiple channels – all in our unified platform.
Make smarter decisions about your business in real-time and hit sales targets with ease.
Sell your products anywhere online and grow your revenue across multiple channels by switching to our enterprise-level e-commerce management platform.
Recent News
Stay up to date
with our news.
Southeast Asia Market Potential
There has never been a better time to scale your e-commerce business
Million
New Online Users
In Southeast Asia In 2020
Million
Online
Consumers
Partners
Meet our clients
Want to explore more?
E-commerce can be complicated, simplify it with aCommerce end-to-end enablement.

















